Features
This is known generally as AR (anti-reflection).
It is a coating process in which a thin dielectric film is formed on the surface of a substrate in a single layer or multiple layers, and the reflectivity of the surface is reduced by light interference.
This increases the transmittance of the substrate, eliminates reflection on the surface and prevents ghosting.
The band of the anti-reflection effect can be selected by manipulating the thickness of the film, the number of layers and the combination of materials.
A wide range of wavelengths is available, from ultraviolet to infrared.
And a wide range of materials can be coated, including glass and infrared crystal materials.
Coating substrates
Provides coatings on glass, resin, quartz, sapphire, ruby, YAG, Si, Ge, ZnSe, ZnS, etc. and other optical crystals.
Applications
Various cover glasses, prevention of ghosting on assembled lenses, sensor windows, etc.
Example applications include coating on curved lens surfaces, fiber end surfaces, cover glass surfaces, and crystal materials (CaF2, Si, Zn, Se).
Example characteristics
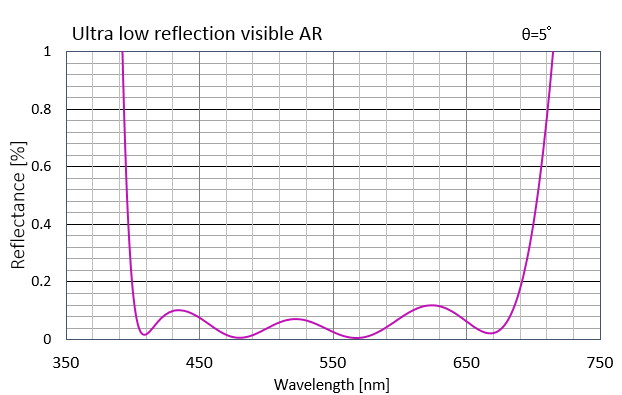
AR coating with an average reflectance of 0.1% or less in the visible light range (420 to 680 nm).
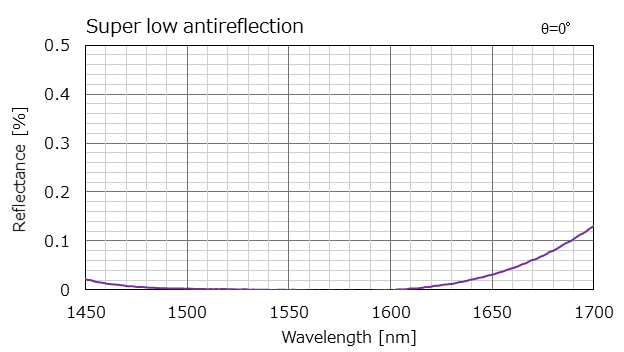
An AR coating with a reflectance of 0.01% or less at near-infrared wavelengths (1550nm).
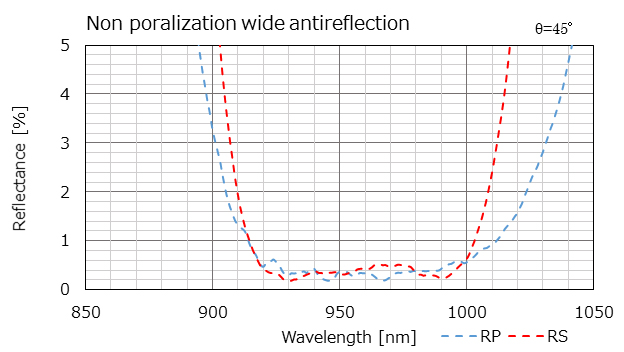
It is a wide AR coating that considers the wavelength separation of P and S polarized light at an incident angle of 45 degrees.
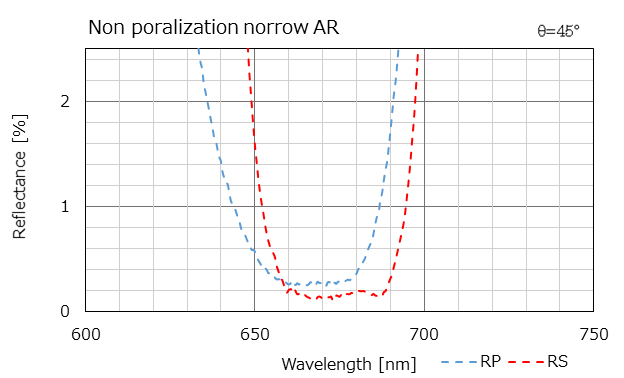
This is a narrow AR coating that considers the wavelength separation of P and S polarized light at an incident angle of 45 degrees.