Filters for fluorescence and Raman analysis
(LASER RAMAN SPECTRUM)
This section introduces various filters used for fluorescence analysis and Raman spectrum measurement equipment.
Fluorescence
analysis |
This is an analytical method that measures the fluorescence emitted from a fluorescent substance when it is irradiated with light. Fluorescent substances that are irradiated with excitation light emit light at lower frequencies than the excitation light as fluorescence. The light that corresponds to the absorption wavelength of the fluorescent substance to be detected is used as the excitation light. Only fluorescent substances can be detected, so the number of substances that can be analyzed is limited. However, fluorescent substances are sometimes attached to the substances to be measured and used as fluorescent labels.
|
Raman
spectroscopy
|
This is an analytical method that uses the Raman scattering light emitted from a substance when it is irradiated with light. Substances that are irradiated with excitation light emit light at both lower frequencies and higher frequencies than the excitation light as Raman scattering light. Raman spectroscopy has a complementary relationship to the absorption seen in infrared spectroscopy. A laser in the visible light region is generally used as the excitation light. The signal for the Raman scattering light is much weaker than that of the excitation light, so the filter used to block the scattered light of the same wavelength as the excitation light must have high performance. |
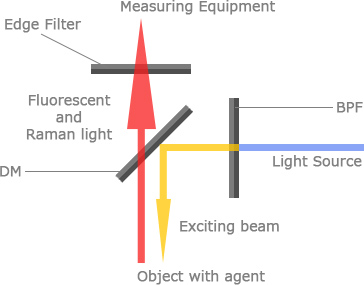
The figure shows the configuration diagram.
(1) Band pass filter : This transmits only the wavelength of light that is to be used as the excitation light.
(2) Dichroic mirror : This reflects the excitation light and transmits the fluorescence and Raman scattering light from the sample.
(3) Edge filter : This removes the excitation light that was scattered by the sample and extracts the fluorescence and Raman scattering light.
Features
| Dedicated film design |
The filters are designed specifically for the intended application. |
Free combination
|
Any wavelength and inclination of the excitation, dichroic, and fluorescence filters can be selected.
|
Low autofluorescence
|
Synthetic quartz is used as the substrate, so there is almost no autofluorescence.
|
High durability
|
The filter film has high durability because a dense metal oxide film is used.
|
High-quality images
|
Excellent image quality can be obtained because we use a film formation process that produces little scattering.
|
Applications
Biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, environment, industry, chemical, Raman imaging spectrographs, Raman process analyzers, Raman microscopes, etc.
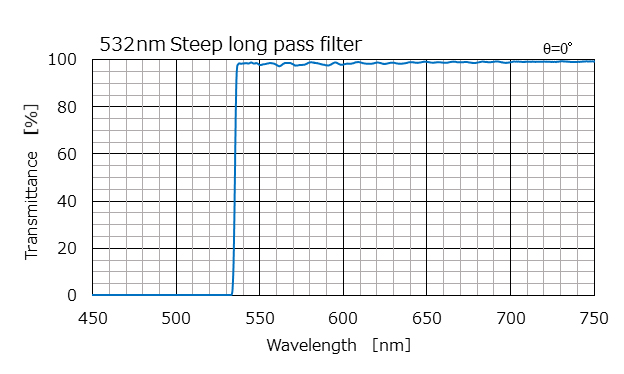
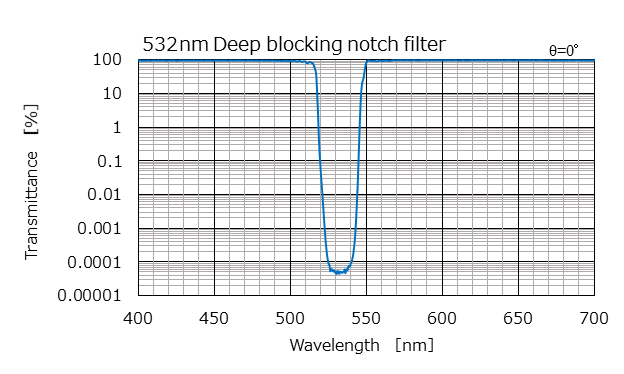
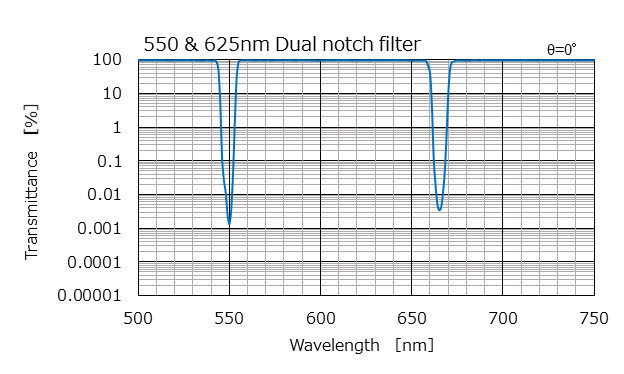
Example characteristics